Substances
Ketamine
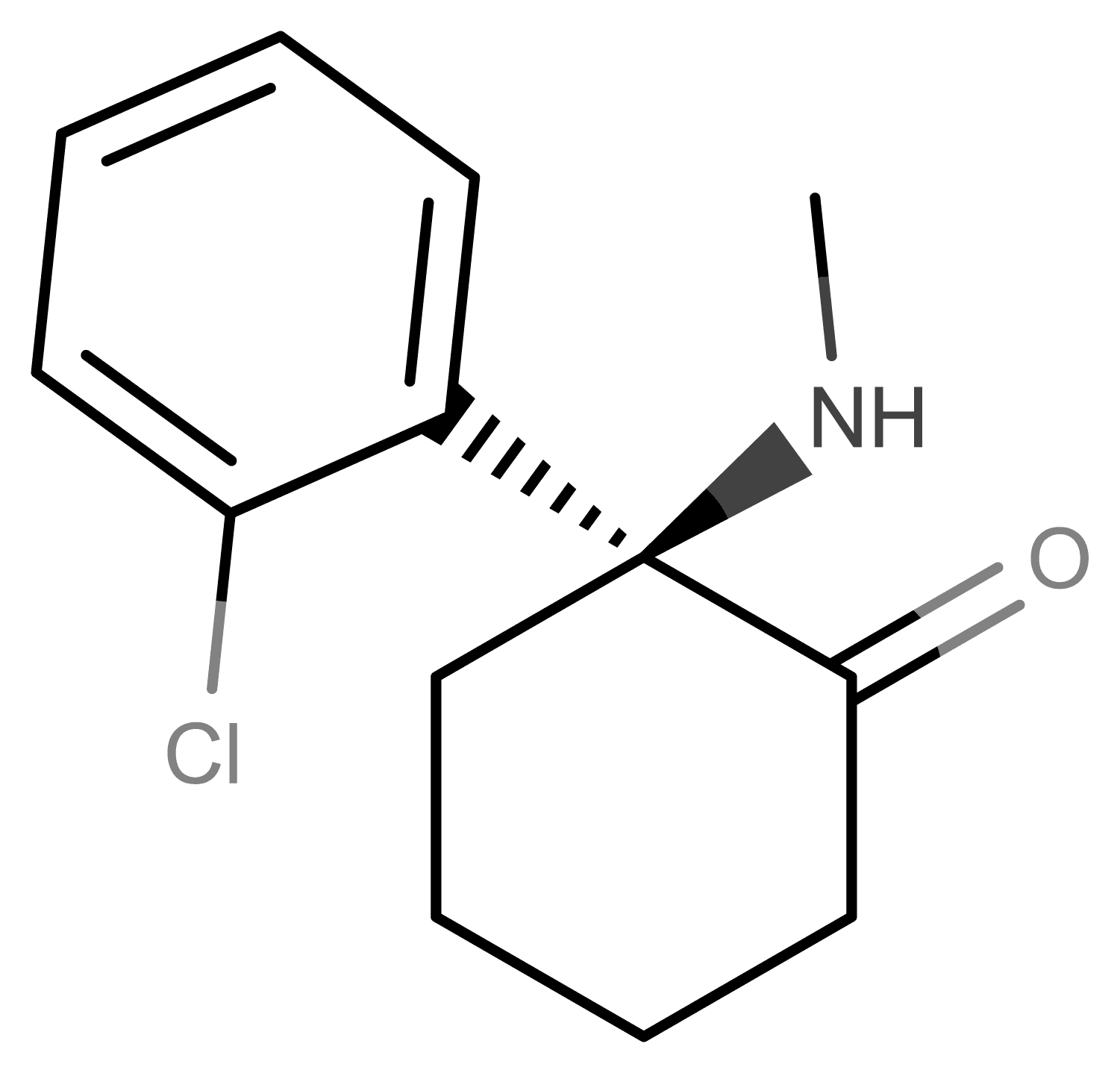
A short acting dissociative anaesthetic and hallucinogen commonly used in emergency medicine. It is the prototypical dissociative, and is widely used at sub-anesthetic doses recreationally. Small doses are comparable with alcohol, while larger doses are immobilising and lead to psychedelic experiences: the "K-Hole."
Harm potential
produces dependence with chronic use and has high abuse potential
Source: PsychonautWiki
Dosage
This dosage information is gathered from users and resources for educational purposes only. It is not a recommendation and should be verified with other sources for accuracy.
oral
light: 50-100mg
common: 100-300mg
strong: 300-450mg
insufflated
light: 10-30mg
common: 30-75mg
strong: 75-150mg
Source: PsychonautWiki
View dosage charts in the KnowDrugs app
Effects
- Low doses: A feeling of drunkenness and well being - similar to the feeling after low doses of alcohol.
- Common doses: Can cause unpleasant feelings because side effects can clearly be felt while the desired full flush effect does not yet occur.
- High doses: Initially, the surroundings frequently seem to fragment and disintegrate. An "out of body" experience might occur. You temporarily lose your ability to taste and smell. Hallucinations are common, music often sounds distorted. You might feel a sensation of lightness. Reduced desire to talk and to express feelings. Your capacity to (re)act and your perception are impeded. Your sensitivity to pain is considerably reduced or even numbed. Very high doeses can induce coma.
- Short-term side effects: blood pressure and pulse are increased, nausea and vomiting can occur (especially when moving). Loss of control over physical movement coordination and muscle movements (ataxia) is possible. Very strong changes in perception can trigger anxiety. After the intoxication, you feel weak for a long time. The intracranial pressure can be increased, visual disturbances, dizziness, increased salivation and motor restlessness can occur.
- In the event of an overdose: Danger of sudden loss of consciousness (mostly with open eyes; the eyes may dry out). Danger of coma and cramp attacks.
- Long-term side effects: memory problems, development of tolerance, psychological dependence and psychosis can be triggered. Frequent use can damage nerves and the brain. Frequent use can further cause uro-nephrological damage such as hematuria, acute renal failure, non-infectious cystitis, interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome) and renal damage linked to a high obstruction (hydronephrosis). Endocrine damages such as increases in cortisol or prolactinemia are reported, as well as liver damage, especially cholestatic cholangitis.
Source: Drugscouts
Interactions
View all interactions in the KnowDrugs app
Tolerance
half
3 - 7 days
zero
1 - 2 weeks
full
develops with prolonged and repeated use
Source: PsychonautWiki